Summa Labs 2026
Our 2026 operations are dedicated to elite teams and world-class organizations. If you are a high-performance individual and want to work with us, contact us below.
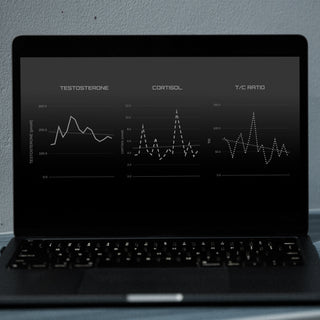
Summa Research Kit
For researchers, performance programs & professional teams.

Athletic Adaptogen
Informed Sport Certified. 100% natural. Sustained energy and faster recovery.
Instagram @summa.labs